If you're wondering "What is Celiac Disease?" before beginning to deal with it, you're not alone. Learn more about this autoimmune disease.
Article courtesy: National Foundation of Celiac Awareness and Dr. Stephen Wangen
Did you know that 3 million Americans have celiac disease, but only about 5 percent of them are accurately diagnosed? Be informed and spread the knowledge!
Celiac disease is diagnosed by measuring damage to the small intestine, either by blood testing or, traditionally, with a biopsy of the small intestine.
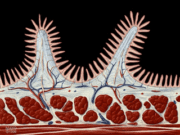
A positive biopsy means that the villi, or small finger-like extensions of the intestinal lining, have been damaged; this is known as villous atrophy. However, recent studies have shown blood testing to be as accurate as a biopsy.
People with celiac disease will show a marked reduction in their villi, almost as if the villi have been worn off. Damage to the villi causes a dramatic reduction in the surface area of the small intestine, resulting in both poor digestion and the poor absorption of many nutrients.
Celiac disease is not the only form of gluten intolerance or allergy. Many people react to gluten by producing elevated IgG antibodies to gluten or wheat, but they do not have damage to the small intestine. Their test results for celiac disease are negative. They become quite frustrated with traditional medicine, with its narrow focus on celiac disease, because they are told that their negative test results meant that they are not allergic or intolerant to wheat, barley, or rye. Yet when they eat a piece of bread they become sick.
Gluten is found in nearly all bread products and all pastas, as well as in most breakfast cereals, cookies, muffins, cakes, soy sauce, pancakes, waffles, soups, sauces, and gravies. Beer, ale, lager, and stout contain gluten. Malt, malt extract, and caramel flavorings, which are used to add flavor to a wide variety of foods, contain gluten.
The treatment for celiac disease and for a gluten intolerance or allergy is identical. It means removing all sources of gluten from the diet. This is not an easy task, because so many of our foods contain gluten. Dietary counseling, such as that provided at the IBS Treatment Center, can make the job easier.
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune digestive disease that damages the villi of the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. What does this mean? Essentially the body is attacking itself every time a person with celiac consumes gluten.
Do you have celiac disease?
Take the celiac disease symptoms checklist »
Celiac disease is triggered by consumption of the protein called gluten, which is found in wheat, barley and rye. When people with celiac disease eat foods containing gluten, their immune system responds by damaging the finger-like villi of the small intestine. When the villi become damaged, the body is unable to absorb nutrients into the bloodstream, which can lead to malnourishment.
Left untreated, people with celiac disease can develop further complications such as other autoimmune diseases, osteoporosis, thyroid disease, and cancer.
You can download a sheet about Celiac Disease facts here.
More Celiac Disease Facts:
Who is at Risk for Celiac?
Celiac disease can affect men and women of any age or race, but there are certain factors that can increase your risk of developing this autoimmune disorder. See more about those at risk for Celiac Disease here.
There are more than 300 symptoms of Celiac Disease, and some people may experience no symptoms at all. Learn about the varying symptoms and how different people are affected.
Diagnosis & Treatment for Celiac Disease:
Celiac disease can be difficult to diagnose because it can present in a variety of different ways. The only treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet. Learn more here.
Many diseases can co-exist with Celiac, such as infertility, migraine headaches, osteoporosis, type 1 diabetes and thyroid disease. Learn more about how they could affect you or a loved one here.







Let Us Know What You Think